|
THE COMPLETE
CARNIVORE DIET GUIDE
Learn how to lose weight, fix your gut and cure autoimmune symptoms with our free Carnivore Diet guide.
|
|
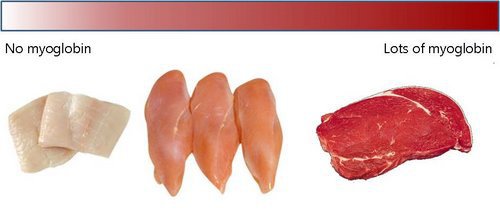
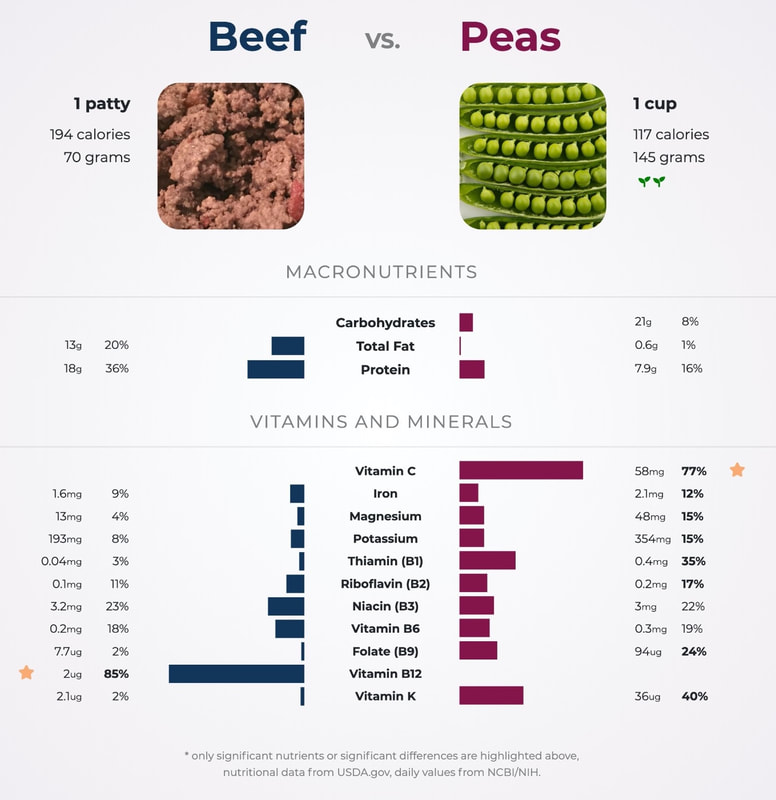
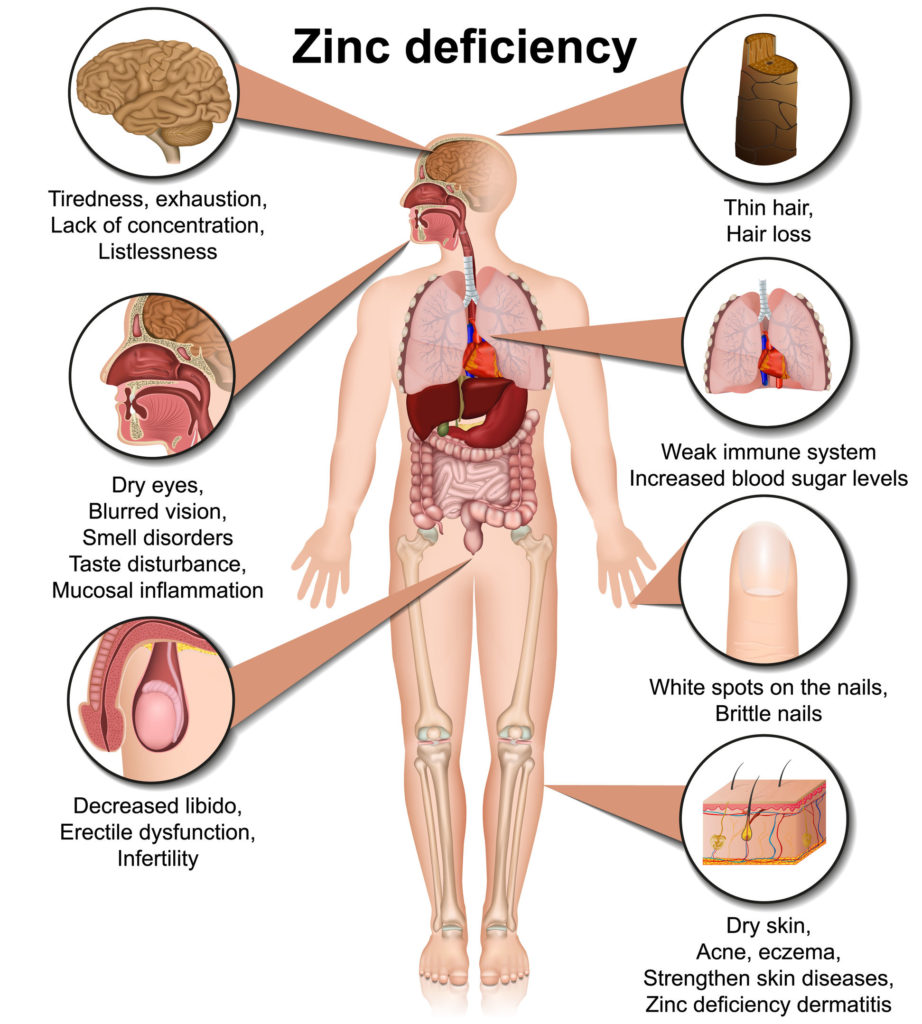
Even if you’re new to the carnivore diet, you’ve probably heard about its health benefits. It can help people struggling with obesity, diabetes, autoimmune disorders like celiac disease, and other chronic health problems. Most people assume that’s because it’s a low-carb diet. And they’re partly right. A low-carb diet is often the solution to chronic health issues. But few people talk about the nutritional value of red meat, which features heavily in the carnivore diet. Is red meat good or bad for you? Are there health benefits to eating red meat? Read on as we uncover the facts. What Is Red Meat? Let’s clarify what is meant by red meat. Meat is often described as ‘white’ or ‘red’. White meat is light-colored when raw. Examples are poultry like chicken or turkey. Red meat is a red color when raw. Examples are beef, pork, or lamb. Red meat owes its pigment to myoglobin, a protein in muscle tissue that binds to oxygen. Red meat has a higher myoglobin content than white meat. Although many people assume that pork is white meat—because it’s light in color—this is incorrect. The Food Safety and Inspection Service in the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) classifies it as red meat. Nutritional Value Of Red Meat Some people are wary of eating meat, especially red meat, thinking it’s unhealthy or bad for the environment. But red meat consumption is not the evil many believe. It’s not killing the planet. Even more importantly, red meats like grass-fed beef contain almost everything your body needs. Red meat doesn’t just offer an increased protein intake, but it also contains essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C. Let’s expand on the nutritional value of red meat: 1. Higher Protein Meat protein is one of the most complete dietary sources of protein you can find in the modern human diet. The protein in red meat varies depending on the source. A 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of red meat like lean beef typically contains 26 grams or more of protein. Animal protein foods such as red meat and eggs, are called complete proteins. That’s because they contain all the essential amino acids needed for the growth and maintenance of the human body. Therefore red meat is a high biological value protein that helps us stay strong and healthy. 2. Iron And Zinc No matter how you slice it, there’s a lot more that’s good about that steak than just the taste. Red meat isn’t just complete protein. It contains iron and zinc, essential minerals the human body needs. Importance Of Iron Iron is responsible for transporting oxygen through the body. Eating iron-rich foods like red meat can also help prevent iron deficiency anemia. The form of iron in animal foods, and most easily absorbed by the human body, is called heme iron. Non-heme iron, found in plant foods, is not as readily absorbed. Red meat contains heme iron and it improves non-heme iron absorption. Importance Of Zinc Red meat contains zinc, needed for immune function, DNA synthesis, and wound healing. Zinc can help with the common cold, shortening its duration or even preventing it altogether. Evidence suggests that zinc might even help protect against acute viral respiratory infections like SARS-CoV-2. 3. Vitamin B12 Vitamin B12 is found primarily in animal foods, including red meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Vitamin B12 plays a key role in:
It’s vital for brain health and nervous system functioning and may even prevent cognitive decline. What About Processed Meats?Processed meats are meats that have been altered in some way to preserve them and extend their shelf life, enhance the taste, or both. Processing methods include canning, curing, fermenting, salting, smoking, and pickling. Examples of processed meat products include bacon, hotdog wieners and franks, and other deli meats and sausages. We agree that these can be very tasty, but does processed meat consumption offer the same nutritional value as unprocessed red meat consumption? The Problem With Processed Meat Many medical professionals agree that processed meats should be eaten in moderation. A Harvard-based study showed that unprocessed red meat did not necessarily increase chronic disease risk, while processed meats did. The problem with many processed meats is not that they don’t contain nutritional value. All meats offer nutrition. The issue is that processed meats tend to be high in sodium, and contain preservatives that can impact our health. This doesn’t mean that you can’t enjoy some bacon with your eggs for breakfast. It means that you should not eat only or mostly processed meats. When it comes to processed red meat consumption, moderation is the key. Red and processed meat differ in the way they impact the body because of the methods used to process and preserve meats. You should severely limit your processed meat intake if you have been diagnosed with, or are at increased risk for heart disease. Despite fears about red meat causing high cholesterol and being detrimental to bone health, the key nutrients red meat contains have proven to be helpful. Health Benefits Of Red Meat Consumption When consumed in moderation, red meat can offer the following health benefits: Nutrient Density: As mentioned above, red meat is a rich source of essential nutrients. These nutrients play important roles in bodily functions such as muscle growth and repair, oxygen transport, immune function, and antioxidant activity. Muscle Health: Red meat is an excellent source of high-quality protein, containing all the essential amino acids needed for muscle maintenance and growth. Eating enough protein, combined with regular exercise, can help support muscle mass, strength, and function. Improved Cognitive Function: The nutrients found in red meat, such as iron zinc, and vitamin B12, are essential for brain health and functioning. Adequate intake of these nutrients is linked to better memory, concentration, and overall cognitive performance. Bone Health: The nutrients found in red meat are important for bone health. Zinc inhibits bone breakdown, and helps in the formation of new bone. Moderation And BalanceShould you eat only red meat for the rest of your life? No. Although the carnivore diet focuses on a high meat intake, it contains a variety of animal foods. Also, the strict form of the carnivore diet is meant to be temporary, while your body heals and you restore your health. You will eventually transition to a more relaxed form of the carnivore diet, at which time the high meat consumption will be offset by a more varied diet. An example is the ketovore diet, which makes allowance for limited fibrous fruits and veggies. Or the paleo diet, which includes nuts, seeds, fruits, and low-carb veggies. Final Thoughts If processed red meat is consumed in excess, especially in processed forms, over a long time, it could pose certain health risks. However, red meat in general can be good for you, thanks to its high nutritional value. By incorporating red meat into a healthy diet, you benefit from this nutrient intake.
Red meat offers very particular and essential nutrients with distinct benefits. Red meat is not only one of the best protein sources, but it’s also high in essential minerals zinc and iron and contains the all-important Vitamin B12. While it’s important to be mindful of the risks associated with excessive meat consumption, adding lean cuts of red meat to a balanced diet is an excellent way to get your essential nutrients in.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Carnivore Diet Recipes & Meal PlansOur Trusted Partners
Popular Guides
|